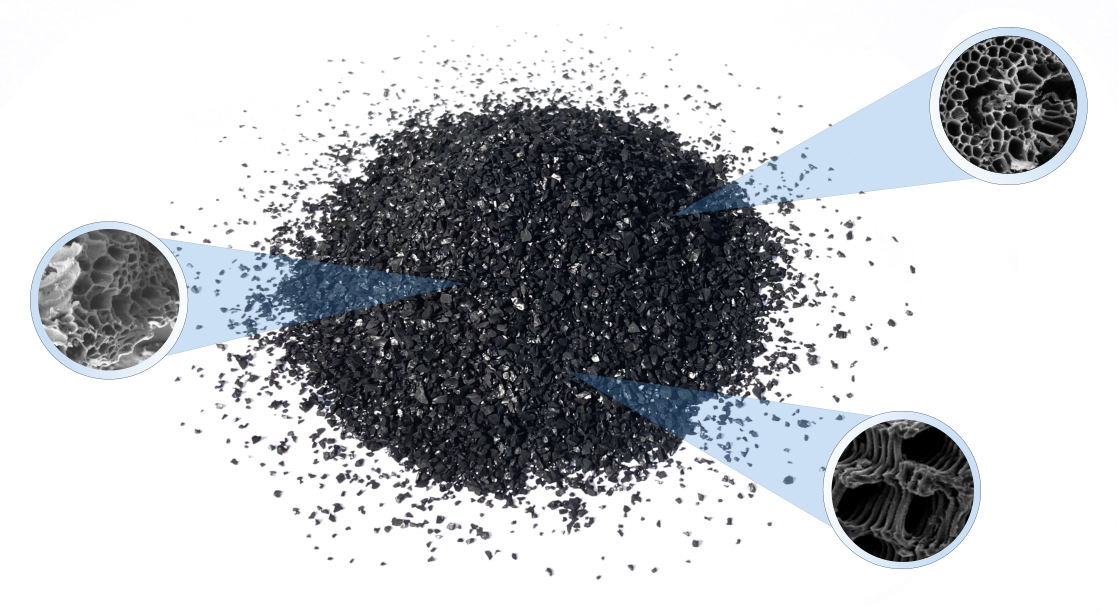
Coconut Activated Carbon
Our core activated carbon ingredient is sourced from Jacobi Carbons because they are world renowned for producing exceptionally high quality coconut activated carbon products. Jacobi owns their own coconut plantation and are able to control every step of production to final product bagging. Their exceptional quality means more water can pass through their media while still producing beyond standard clean water for point-of-entry (large filtration tanks) and point-of-use (smaller filtration tank for direct consumption).
Filter, Reduce, Adsorb chlorine, chloramine, hydrogen sulfide, organic compounds, chlorinated by-products (chloroform, trihalomethanes (THM’s), and many others), taste, odor, and so much more.

What Does Activated Carbon Adsorb?
Organic Compounds
highly effective at removing organic contaminants:
-
Pesticides & herbicides (Atrazine, Glyphosate (Roundup), 2,4-D)
-
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) – solvents, fuels, industrial chemicals (Benzene, Toluene, Xylene,
Formaldehyde, Acetone, Petroleum hydrocarbons). Pharmaceutical Residues (Antibiotics, Hormones (estrogen, BPA), Painkillers (ibuprofen, acetaminophen)) -
Disinfection byproducts like Trihalomethanes (THMs) and Haloacetic acids (HAAs)
-
Chlorine-based compounds (sodium hypochlorite, chloramines)
-
Ozone (O₃) – breaks down organic contaminants
-
Total Organic Carbon (TOCs) – decaying plant/animal matter
-
Removes chlorine taste and odor from water.
While not all heavy metals bind easily, activated carbon can adsorb:
-
Mercury
-
Lead (Pb) – especially when combined with other media like KDF
-
Cadmium (Cd)
-
Copper (Cu)
-
Nickel (Ni)
-
Chromium (Cr) – depends on oxidation state
- Arsenic (As) – limited effectiveness (works better with iron-enhanced carbon)
-
Eliminates hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg smell)
-
Filters out fine particles, residual disinfectants, and turbidity, rust and silt
Activated carbon does not kill bacteria/viruses, but it can:
-
Remove organic matter that bacteria feed on
-
Improve the effectiveness of UV or other disinfection methods
Key Advantages over other activated carbon suppliers and brands:
High Adsorption Capacity – Optimized pore structure and density maximize contaminant removal, targeting:
-
Low molecular weight organic compounds
-
Rapid Dechlorination – Quickly neutralizes chlorine and free chlorine for cleaner, safer water.
-
Low Turbidity Output – Ensures crystal-clear filtered water with minimal particulates.
-
Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S)
What Activated Carbon Does Not Remove Effectively
-
Dissolved salts (e.g., sodium, fluoride, nitrates – requires reverse osmosis)
-
Hard water minerals (calcium, magnesium – needs a water softener)
-
Most viruses & bacteria (requires UV, boiling, or chemical disinfection)
For best results, combine activated carbon with other filtration methods (KDF, reverse osmosis, or ceramic filters) to target a broader range of contaminants.







